A bulging disk in the back is a condition where the disks between the vertebrae bulge out and put pressure on the nerves. Bulging disks can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. Treatment for a bulging disk depends on the severity of the condition. Rest and over-the-counter pain medication may be all that is needed for mild cases. Physical therapy, steroid injections, and surgery may be necessary for more severe cases.
What are Bulging Discs?
Bulging discs are a common occurrence. They can occur in the spine, neck, or other areas of the body. This condition is usually caused by an injury to the vertebrae that causes friction and pressure on the discs.
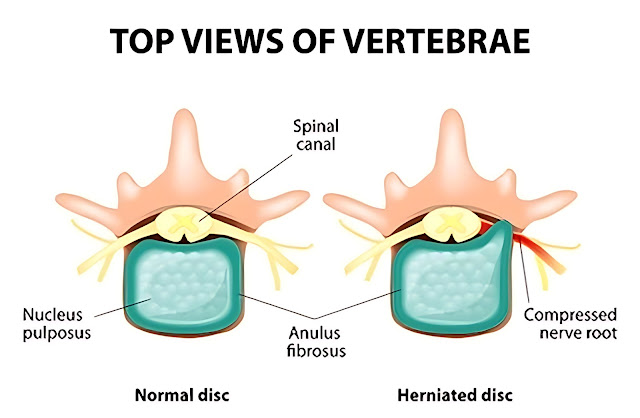
A bulging disc is defined as a protrusion that pushes against another part of the spine that’s not designed for this kind of pressure. The discs are located between each vertebrae and act as shock absorbers for your spine.
Bulging discs can be caused by osteoarthritis, car accidents, falls, and sports injuries such as football and basketball injuries. The most common symptom of bulging discs is a pain in your low back or buttocks area that worsens with sitting or standing up too quickly.
Other bulging disc symptoms include:
- Stiffness when sitting
- Pain when twisting your hips or bending over
- Weakness when lifting objects that you normally don’t have problems with
- Numbness in your buttocks area
Contained Disc vs. Non-Contained Disc Disorders in the Back or Neck
The contained disc disorder is a condition that involves a herniated disc, which can result in pain and discomfort due to the bulging of the disc against its normal position. This type of injury may be more severe than a non-contained disc because it affects the nerve itself, which can cause numbness, tingling, and even weakness in the arm or leg. If a contained disc goes untreated for too long, it may lead to permanent nerve damage that causes permanent weakness in those areas as well.
The term "non-contained disc" refers to a disc that has not ruptured or herniated. In these cases, the nerve root is still intact and there are no symptoms. These types of discs will typically heal up over time and be asymptomatic.
The non-contained disc disorder, on the other hand, involves a bulging of the outermost layer of cartilage (annulus fibrosis) on top of underlying vertebrae. This type of disc disorder does not cause pain because there is no actual bulging like in a contained disc disorder; instead, it is more like fluid buildup or inflammation in this area.
Bulging Disc and Herniated Disc Difference
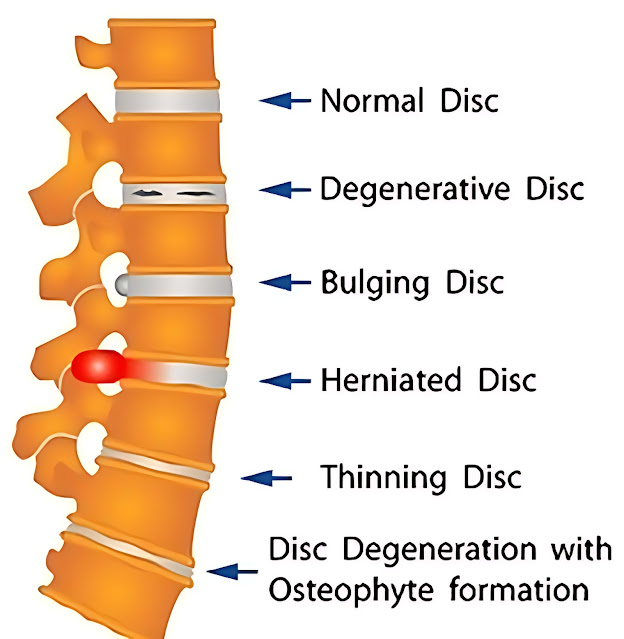
When the gel-like center of a disc ruptures through a weak area in the tough outer layer and squeezes into the spinal canal, this is referred to as a herniated disc.
A bulging disc occurs when the outer layer of the disc is pushing out, but the inner gel has not yet ruptured.
Types of Herniated and Bulging Discs
There are two main types of herniated discs: cervical and lumbar. Cervical herniated discs occur in the neck, while lumbar herniated discs occur in the lower back. Both types of herniated discs can cause severe pain and other symptoms.
Bulging discs are a less serious type of disc injury. Bulging discs occur when the outer layer of the disc bulges outwards, but the inner layer does not rupture. Bulging discs can cause pain and other symptoms, but they are not as serious as herniated discs.
Cervical Bulging Disc- Neck
The cervical bulging disc (CBD) is a condition where the spinal cord becomes compressed at the neck. It is often caused by trauma, degenerative changes, or even tumors. When the spinal cord is compressed, it causes pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, and sometimes paralysis. There are many different types of CBD, each with its symptoms and treatment options.
To diagnose a CBD, doctors need to perform a physical exam and imaging tests. A physical exam includes looking at the patient's posture, reflexes, sensation, muscle tone, and range of motion. Imaging tests may include X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasounds. These tests help doctors determine if the CBD is due to a tumor, injury, or other cause.
Treatment options for a CBD depend on what type of CBD it is. If the CBD is due to trauma, a bulging disc operation may be necessary. In cases where CBD is due to degeneration, medication may be prescribed. If the CBD is caused by a tumor, radiation therapy may be recommended.
Lumbar Bulging Disc- Lower Back
A lumbar bulging disk (LBD) is a condition where the spinal discs between the vertebrae in the lower back become compressed. This causes pain and discomfort in the lower back area. LBDs are often caused by poor posture, prolonged sitting, or repetitive lifting.
How do I know if I have a lumbar bulge?
If you have any type of back pain, then you may have a lumbar disc bulge. You should always consult a doctor before trying to treat yourself. However, here are some ways to tell if you have a bulging disc:
• If you feel pain in your lower back while standing or walking, you may have a bulging disc.
• Your back feels stiff after being seated for long periods.
• You experience numbness in your legs or feet.
• You experience tingling sensations in your hands and arms.
• You experience weakness in your legs.
• You experience difficulty sleeping at night.
What are the symptoms of a lumbar bulged disc?
The following are the symptoms of a bulging disc:
• Pain in your lower back
• Numbness in your leg
Circumferential Disc Bulge
A circumferential disc bulge is a type of herniated disc that occurs when the outer layer of the disc tears and the inner layer bulges out. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. Treatment options include physical therapy, steroid injections, and surgery.
Asymmetric Disc Bulge
Asymmetric Disc Bulge (ADB) is a type of disc bulge that is characterized by an asymmetry in the shape of the bulge. ADB is typically caused by an imbalance in the distribution of mass in the disc, which can be due to a variety of factors such as a central mass concentration, an offset central mass or an unequal mass distribution in the disc. ADB can also be caused by a warp in the disc.
Herniated and Bulging Disc Risk Factors
The risk factors for herniated discs include:
Age. As you age, your spine becomes more brittle as it stiffens due to loss of moisture and natural lubrication. This can lead to pressure on nerves and herniation at the site of pressure from a bulging disc.
Weight loss. It's not uncommon for people who lose weight over time to experience pain in their backs because their spine has lost some of its natural paddings and is more vulnerable to injury.
Injury history. Falls or trauma can damage discs in your spine even if you've never experienced symptoms before such as nerve pain or weakness in an arm or leg.
Bulging Disc Risk Factors
Bulging discs can be caused by repetitive movement or injury. They may also be caused by osteoarthritis, which is a degenerative joint condition that causes bones to wear down over time. A bulging disc can cause pain when you press on it or turn your head to one side.
Treatment for Bulging Discs
Bulging discs are a condition where the disc between the vertebrae becomes bulged outwards causing pain and discomfort. There are various treatment methods for bulging discs. These treatments may involve medication, physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and surgery.
Medication
The first line of defense for treating bulging discs is medications. Medications can help relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation. However, they do not treat the cause of the problem. If you have tried medication without success, then you should consider seeing a doctor about further treatment options.
Physical Therapy
If you have been experiencing back pain for a long time, you might want to try physical therapy. Physical therapists use different techniques to help alleviate pain and improve movement. They can teach you exercises to strengthen muscles and increase flexibility. In addition, they can provide advice on how to avoid aggravating the injury.
Chiropractic Care
A chiropractor uses manual adjustments to realign the spine and correct any imbalances. Bulging disc chiropractors often recommend spinal manipulation to patients who suffer from chronic back pain. A chiropractor can adjust the spine to restore proper alignment and function.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting needles into specific points along the body to stimulate healing. Acupuncturists believe these points are linked to organs and meridians. By stimulating these points, acupuncturists aim to balance the flow of qi (energy) throughout the body.
Spinal Manipulation
Spinal Manipulation is a treatment for bulging discs that involves the application of manipulative forces to the spine. The goal of Spinal Manipulation is to reduce pain and improve function by correcting the alignment of the spine. Spinal Manipulation is typically performed by a chiropractor, osteopath, or physiotherapist.
Spinal Manipulation is a safe and effective treatment for bulging discs. A systematic review of the evidence found that Spinal Manipulation is more effective than sham treatment, with no treatment, or usual medical care for the treatment of low back pain.
The evidence also suggests that Spinal Manipulation is as effective as other common treatments for bulging discs, such as massage, acupuncture, and exercise.
Surgery
Bulging disc surgery is considered only if conservative measures fail to resolve the issue. Surgery can be done to remove damaged parts of the disc or fuse two adjacent vertebrae.
Causes of a Bulging Disc
As a disc age, it begins to shrink and get thinner. This is normal and occurs as a result of the water content in the disc dries out. This can cause small tears in the disc's outer layer, called the annulus fibrosus. When the annulus fibrosus tears, the gel-like center of the disc, called the nucleus pulposus, can push through the tear. When this happens, the disc is said to bulge.
It can take many years for a disc to degenerate to the point where it bulges. However, once a disc bulges, it can become worse over time.
In some cases, a disc may bulge as a result of an injury. This can occur if you lift something heavy or awkwardly twist your back. A disc may also bulge as a result of degenerative changes in the spine, such as osteoarthritis.
Herniated Disc Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a herniated disc can include:
- Arm or leg pain — sharp, shooting, or searing, or a dull, aching sensation
- Numbness or tingling in your arms or legs
- Weakness in your arms or legs
When to see your doctor
If you have symptoms of a herniated disc, contact your bulging disc treatment doctor. If you have sudden or severe back pain or pain that radiates down your leg or arm, call for emergency medical assistance.
Diagnosis for Herniated and Bulging Disc
Herniated disks and bulging disks are diagnosed in several ways. The doctor will ask the patient about symptoms, do a physical examination, and order tests. An MRI scan is the best test to diagnose a herniated disk. A CT scan can also be used to diagnose a disk problem.
Final Thoughts
Bulging disks are a common cause of low back pain. The disk is a cushion of sorts between the bones in your spine, and when it bulges it puts pressure on the nerves in your spine which can cause pain. If you think you may have a bulging disk, it's important to see a doctor so they can properly diagnose and treat the problem. Treatment for a bulging disk usually involves rest, ice, heat, and over-the-counter pain medication. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged disk.
Comments
Post a Comment