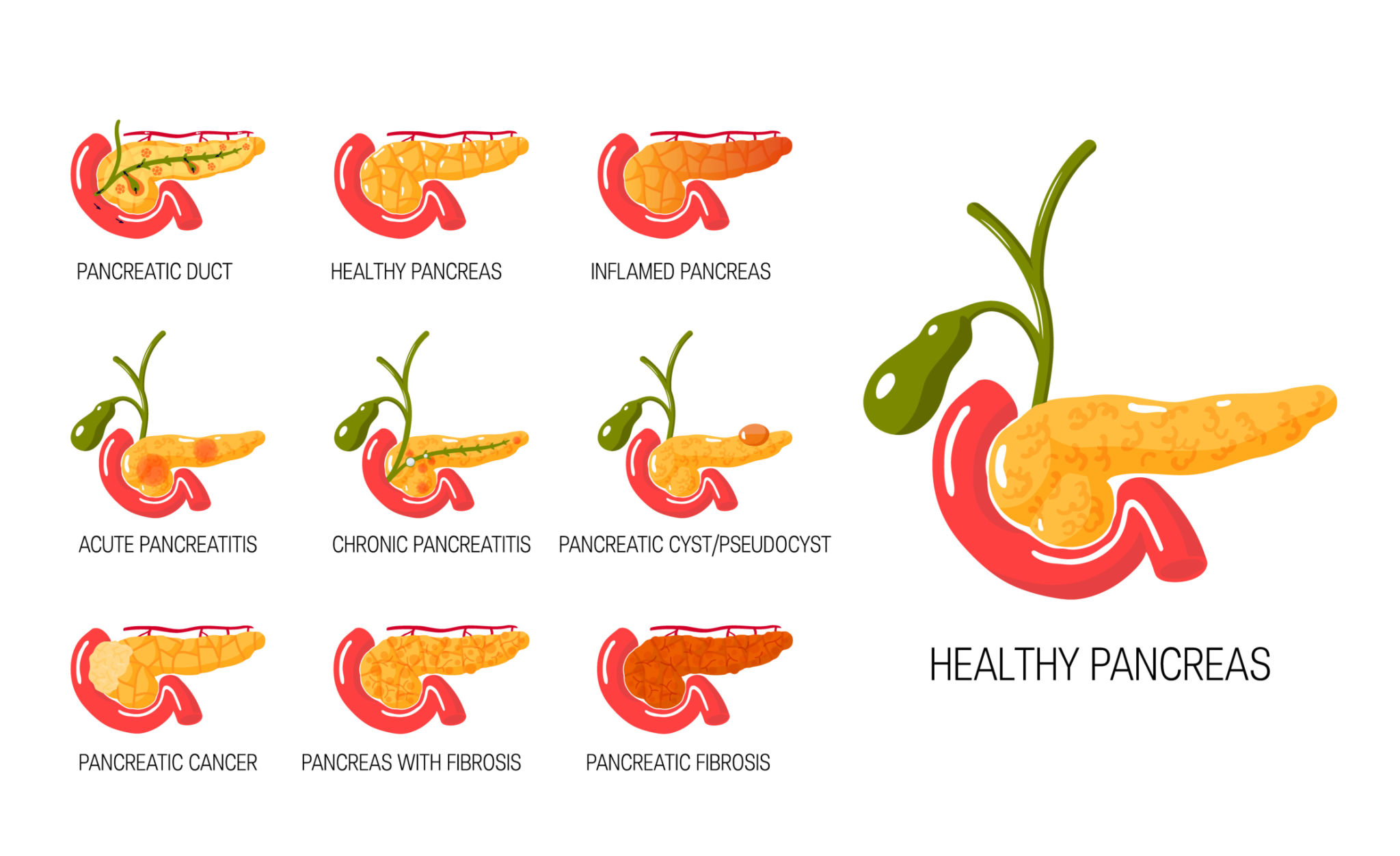
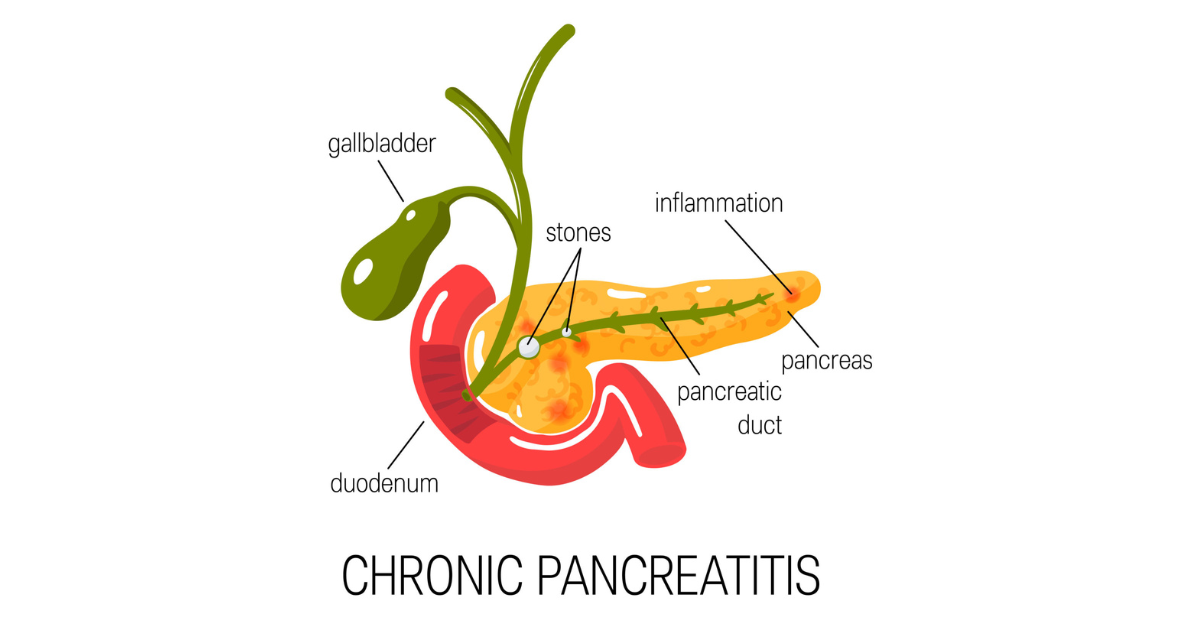
Chronic pancreatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the pancreas. It can cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, and other symptoms. The condition usually occurs after long-term alcohol abuse or excessive consumption of certain medications.
Chronic pancreatitis is caused by damage to the pancreas due to chronic alcoholism, gallstones, trauma, autoimmune diseases, or genetic disorders. In some cases, no cause can be identified.
Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by persistent abdominal pain, maldigestion, steatorrhea (fatty stools), and elevated serum amylase levels. Diagnosis is confirmed by imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery.
Difference between acute and chronic pancreatitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas caused by excessive alcohol consumption, gallstones, trauma, infection, or autoimmune disease. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chills, and weight loss.
In some cases, patients may experience jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin), dark urine, and fatigue. Acute pancreatitis is often diagnosed after a patient presents with these symptoms.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is inflammation of both the exocrine and endocrine portions of the pancreas. Symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Patients may also have diabetes, steatorrhea (fatty stools), and weight loss. Chronic pancreatitis is often diagnosed based on the results of blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsy.
Depending on the type of pancreatitis you have to visit gastroenterologist.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
1. Abdominal pain
The abdominal pain associated with chronic pancreatitis is often described as dull, constant, cramping, or stabbing. It may radiate to the back or front of the abdomen. Pain may occur at rest or after eating, drinking, or moving around.
2. Nausea/vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are frequent symptoms of chronic pancreatitis. These symptoms may be due to the inflammation of the pancreas or the bile ducts.
3. Weight loss
Weight loss is a common symptom of chronic pancreatitis. It occurs because the body cannot digest food properly.
4. Jaundice
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin) is caused by the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a breakdown product of red blood cells. In people with chronic pancreatitis, the liver produces more bilirubin than normal. As a result, jaundice may develop.
5. Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of many illnesses. Chronic fatigue is a persistent tiredness that does not improve with sleep. It may worsen over time.
6. Diarrhea
Diarrhea is the passage of loose stools. People who have chronic pancreatitis may experience diarrhea several times per day.
7. Constipation
Constipation is the infrequent passage of hard stool. People with chronic pancreatitis may experience constipation several times per week.
Causes of chronic pancreatitis
1. Alcoholism
Alcohol consumption causes damage to the pancreas. Chronic alcohol abuse damages the pancreas over time, leading to inflammation and scarring. As the pancreas becomes damaged, it loses its ability to produce enzymes necessary for digestion. These enzymes help break down food into smaller particles that can be absorbed by the body. When these enzymes are not produced, they cannot properly digest food.
2. Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cells of the pancreas. Symptoms may include pain in the upper abdomen, weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, fever, and back pain. Diagnosis is often delayed until symptoms worsen.
3. Gallstones
Gallstones are small stones that develop inside the gallbladder. Most people have them at some point in their lives. Gallstones are formed when bile gets trapped in the gallbladder and hardens. Bile is a fluid that helps break down fats and oils in the digestive tract. If the gallbladder does not empty regularly, the bile builds up and forms a stone.
4. Diabetes
Diabetes occurs when the body's inability to use insulin properly results in high levels of glucose in the blood. Insulin is a hormone that regulates sugar levels in the blood. Type 1 diabetes develops when the body stops producing insulin. Type 2 diabetes develops when the body doesn't respond effectively to insulin. Both types of diabetes cause long-term complications if left untreated.
5. Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia refers to abnormally high cholesterol levels in the blood. High cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease. People who have hyperlipidemia tend to have higher triglyceride levels than normal. Triglycerides are fat molecules that circulate in the bloodstream.
6. Obesity
Obesity is defined as having excess body fat. Excess body fat increases the risk of many serious medical conditions including heart disease, stroke, sleep apnea, certain cancers, and osteoarthritis.
7. Other Causes
Other causes of chronic pancreatitis include trauma, infection, autoimmune disorders, genetic factors, medications, and idiopathic causes.
Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis
Diagnostic tests for pancreatitis include blood tests, imaging studies, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), and ultrasound.
Blood tests look at levels of amylase and lipase enzymes in the blood. Imaging studies include computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasonography. ERCP involves inserting a tube down the throat and into the duodenum (first portion of the small intestine).
A dye is injected into the duodenum and then x-rays are taken. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of internal organs.
Treatment for chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis treatment may be recommended for patients with persistent pain that cannot be controlled otherwise.
1. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)
This is the first line of treatment for patients who have chronic pancreatitis. PERT is a medication that contains enzymes that help break down fats and starches in the digestive tract. These medications are given orally and are designed to replace the function of the pancreas.
2. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
ERCP is a procedure where a tube is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach. A small amount of contrast dye is injected into the duodenum, which travels through the bile ducts and into the pancreas. X-rays are then taken to check if any blockages exist.
If no blockage exists, the gastro surgeon in Coimbatore may perform a sphincterotomy, which involves cutting away parts of the sphincter muscle that controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juices.
3. Surgery for chronic pancreatitis
Surgery is only considered after ERCP fails. In some cases, surgery is necessary to remove the gallbladder or portions of the pancreas that are damaged.
Can chronic pancreatitis be prevented?
If you have a family history of the disease, however, you should talk to your doctor about screening tests and should follow certain precaution methods
1. Avoid alcohol consumption
Alcohol consumption may cause damage to the pancreas and lead to chronic pancreatitis. Alcohol intake should be avoided if possible. If you do drink alcohol, limit yourself to no more than two drinks per day.
2. Stop smoking
Smoking cigarettes causes inflammation and irritation in the pancreas. Smoking cessation is recommended.
3. Eat a balanced diet
A well-balanced diet is necessary for good health. A high-fat diet can increase the risk of developing chronic pancreatitis.
4. Exercise regularly
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces stress levels. Regular physical activity can help prevent chronic pancreatitis.
5. Maintain a healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle includes eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, avoiding alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy bodyweight.
The average length of time between diagnosis and death due to CP is about 5 years. However, some people have lived with the condition for decades without developing complications.
Chronic pancreatitis life expectancy
Chronic pancreatitis is a serious and life-threatening condition that affects the pancreas. While there is no cure for chronic pancreatitis, early diagnosis and treatment is essential for managing the condition and preventing further damage to the pancreas.
If you think you or someone you know may have chronic pancreatitis, it is important to see a stomach specialist as soon as possible. With the right treatment, you can live a normal, healthy life.

Comments
Post a Comment